*If you are moderately obese, discuss with your healthcare provider whether Lo Loestrin Fe is appropriate for you.
>

Patch
>

Diaphragm
>
Spermicide/Jelly
>
Intrauterine Device (IUD)
>

Male Condom
>
Female Condom
>
Vaginal Ring
>
Shot (Injection)
>
Estrogen is a key component in many hormonal birth control options.
5 THINGS YOU DIDN'T KNOW
about everyone’s favorite
pregnancy prevention method:
BIRTH CONTROL PILLS.

You’ve heard about them. Your friends use them. You might have even tried ’em or use them yourself. But whatever your experience, here are some facts you might not know about those glorious little pills:
1

The FDA approved the Pill as an oral
contraceptive in 1960. That’s 6 decades
of empowering women!
2
A national survey found that birth control pills are used by over 10 million women in the U.S.
3

It's possible to stay on a birth control
pill for a number of years. However,
it's important to consult with your doctor
as birth control pills may not be
appropriate for patients with certain conditions.
4
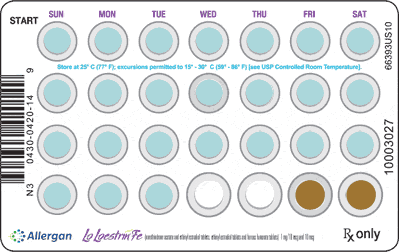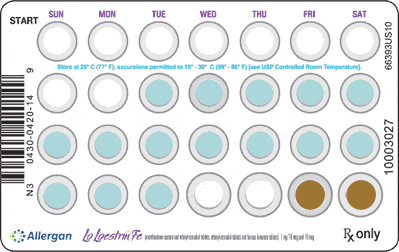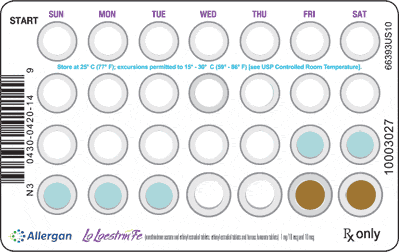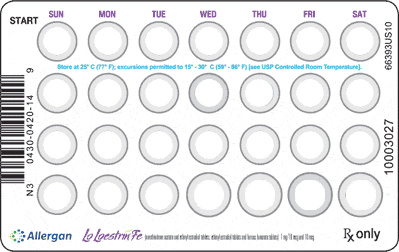
There are different types of birth control pills, and each can have a different formulation when it comes to the type and dose of estrogen or progestin. Good to have options!
5

In 1993, The Economist named the birth control pill as one of the Seven Technological Wonders of the Modern World. Mic drop.
So it’s pretty evident that birth control pills have made a big difference in the world of women’s health. Want to learn more?


